Date:
Abstract: This paper describes the scientific selection of in vitro dissolution test conditions to improve its correlation with in vivo bioavailability, as well as the requirements for pharmaceutical preparation technology. The development status and problems of solid medicine preparation were proposed.
Key words: dissolution; Bioavailability; Bioequivalence; A pharmaceutical preparation; Quality control
CLC Number: TQ460.7 + 2; R969 Reference Code: A Paper No. : 1001-8255(2005)07-0447-05
For pharmaceutical solid preparation, what is the difference between domestic medicine and imported medicine? Why do patients have different curative effects after taking certain drugs with the same dosage form 1? What test method, what test index can be used to scientifically and effectively evaluate the difference in clinical efficacy between domestic and imported drugs? Does it have to be at the final clinical stage? Is it just the conditions of production -- that is, the conditions of production that are GMP certified?
1. The influence of internal environment on drug absorption
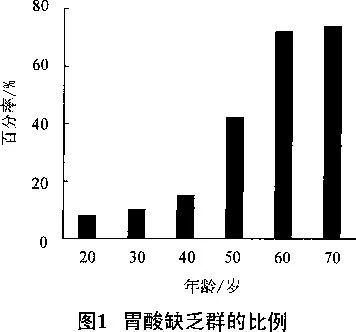
The main part of human body to absorb drugs is digestive tract. The internal environment is normal, there is a normal amount and normal pH of gastric acid and intestinal fluid in the gastrointestinal tract; The body environment is abnormal or weak, the amount and pH of stomach acid and intestinal fluid will be different. It has been reported 2 that the pH range of the liquid in human digestive organs is 1.2 ~ 7.6 in the stomach and 3.1 in the duodenum ~ 6.7, small intestine 5.2 ~ 6.0. In people over 50 years of age, there were changes in stomach acid and intestinal fluid (Figure 1).
Received: 2005-05-08
About the author: Xie Mufeng (1973), male, master, engaged in the research of new drug review and quality standards. 2003.8 ~ 2004.2 in Japan's national institute of medical 薬 product food hygiene 薬 department of education.
Tel: 021-64703139 × 135 or 132,013764153662
E-mail:xiemufeng@sina.com.cn
1.1 Evaluation of drug efficacy
The evaluation criteria of good efficacy of drugs are: any patients suffering from the disease (regardless of gender, age, physical condition, internal environment) have certain curative effect and action after taking the drug, that is, the treatment is effective and wide application. Otherwise, it will lead to: the same drug of the same dosage form produced by different manufacturers, has different efficacy for different patients; The same drug from the same manufacturer has different therapeutic effects on different patients, that is, the therapeutic effectiveness is low and the range is narrow.
Efficacy is closely related to bioavailability. Drugs with low bioavailability may only have certain disintegration, dissolution and absorption in one internal environment (such as those with normal gastric acid), and have no significant effect on other patients. This is at the heart of the intrinsic quality differences in drugs.
1.2 Dissolution test and evaluation criteria
Although bioavailability is ultimately measured in terms of clinical efficacy, it can be largely evaluated by in vitro dissolution tests. In vitro dissolution test refers to the dissolution rate and degree of a drug from a solid dosage form such as tablet or capsule in a specified medium under certain test conditions. Since it was first introduced by the United States in 1967, it has been rapidly popularized. Now it has become an important index for the quality control of pharmaceutical products and an extremely important means to evaluate the prescription and production process of pharmaceutical products.
To improve the correlation between in vitro dissolution test and in vivo bioavailability, and to establish the conditions of dissolution test to evaluate the quality of the preparation scientifically and effectively is one of the research emphases.
The rotating basket, paddle and rotating speed in the dissolution test device can be used to simulate the peristalsis of human stomach and small intestine. The digestive fluid in human body is usually simulated by the following four dissolution media:
A solution of pH 1.2 (2.0g sodium chloride, dissolved in appropriate amount with water, 7ml hydrochloric acid, diluted to 1000ml with water, to obtain). At present, foreign countries tend to adopt this preparation method, which is different from 0.1mol/L salic acid solution (9ml hydrochloric acid → 1000ml) commonly used in our country.
pH 4 acetate buffer 0.05mol/L acetate -0.05mol/L sodium acetate (16.4∶3.6). The ion concentration was lower than that recorded in the appendix of Chinese pharmacopoeia. At present, the dissolution tests in this medium are seldom studied in our country.
(2) pH 6.8 phosphate buffer solution (3.4g potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 3.55g anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate, dissolved with water in appropriate amount to 1000ml, then diluted twice, to obtain). The ion concentration was also lower than that recorded in the appendix of Chinese pharmacopoeia.
(3) Water is a quality drug, in the use of a certain dissolution device and speed (these conditions also need to be studied and demonstrated in detail), in the above four dissolution media should have a certain dissolution curve, so as to ensure that the drug used in human body, can have a certain dissolution or release in a variety of internal environment, that is, for patients with any constitution have a certain effect. If 4 (or more) curves are combined, they can also be represented by the three-dimensional diagram of time, dissolution amount and dissolution medium 3 (see Figure 2), which should be smooth and have a certain slope.
However, if the preparation dissolves well only under the condition of pH 1.2, it can only ensure the good absorption of patients with normal gastric acid, while patients with gastric acid deficiency may be poor. The peristalsis degree of gastrointestinal tract varies greatly among individuals. In the drug dissolution test, if the preparation can only be dissolved under the conditions of paddle method and 100r/min, then it may only be released and absorbed in the body of the body with strong function, and in the body of the weak, it will not be released and absorbed; However, if there is a "high and certain" dissolution curve in the above four dissolution media under the conditions of paddle method and 50r/min, then the patient will have a high and certain bioavailability, that is, a wide range of efficacy, no matter what the situation in the body is. See Figure 3.
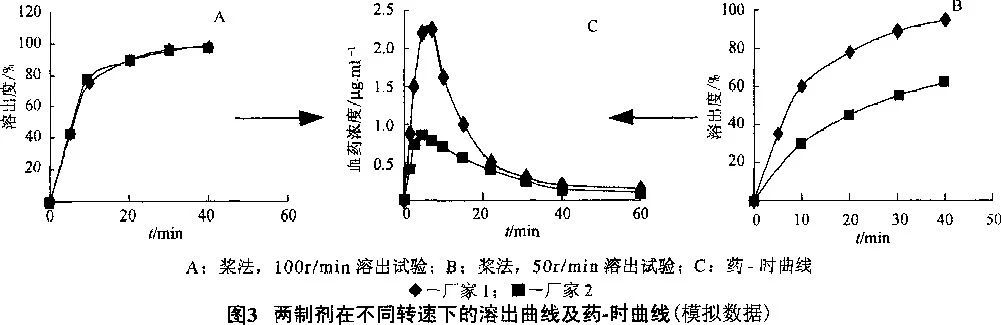
Carbamazepine tablet, for example, Japan's "medical 薬 product quality for medical use intelligence collection" [Japanese ministry, namely Japan the reference preparation directory (Orange Book), hereinafter referred to as: The dissolution test conditions of the preparation (specification is 100mg, carbamazepine is insoluble in water) in the above four media are paddle method, the rotation speed is 75r/min, the dissolution medium is 900ml, and the samples are determined at 5min and 30min, respectively. The limits are not more than 60% (to prevent sudden release) and not less than 70%, respectively. Since there is no reference preparation list in China, refer to Chinese Pharmacopoeia.
The method under carbamazepine tablets in 2005 edition was as follows: the second method (paddle method) was used, the rotation speed was 150r/min, 0.1mol/L hydrochloric acid was 1000ml as the dissolution medium, and the limit was 65 %. The author once tested a domestic carbamazepine tablet according to the requirements of the Japanese reference catalog, and the results showed that the four curves were far different from the dissolution curves reported in the Japanese reference catalog.
The differences of dissolution test conditions, the choice of dissolution medium and the formulation of limits will inevitably lead to different requirements for prescription screening and preparation technology. The test conditions of dissolution can be set up strictly, which can promote the improvement of preparation technology.
Japan "drug quality evaluation" (薬 product quality review 価) project description
The following problems have also occurred in the clinical use of drugs in Japan.
(1) How to make the same type of drug produced by different manufacturers on the market have the same bioequivalence for any patient?
(2) How to use in vitro dissolution test to evaluate or replace in vivo bioavailability more scientifically and effectively?
(3) How to improve bioavailability by developing scientific and reasonable dissolution test conditions and methods? That is, how to promote the improvement and improvement of the production process, so as to improve the internal quality of drugs and improve the curative effect?
(4) How to ensure that many generic drugs have the same quality and clinical efficacy as the original products more effectively and conveniently?
(5) How to make the late mass production of drugs and clinical trials Do pilot-scale drugs have the same quality and bioavailability?
(6) How to ensure that bioavailability tests or clinical trials are exempted for the imitation of high-throughput, high-water solubility solid preparation drugs? To this end, the pharmaceutical Administration Department of Japan's Ministry of Health launched the project of "Drug Quality Reevaluation" in 1998.
2.1 Purpose and technical core of the "Drug Quality Reevaluation" Project The purpose of the project is to ensure that oral solid preparations are effective for different patients
All of them had high bioavailability. Make the same drug produced by different enterprises have the same bioavailability; The internal quality and effectiveness of drugs were re-evaluated by existing technical means. The content is: to evaluate the quality of drugs through comprehensive, detailed and in-depth in vitro dissolution test research and determination; According to the requirement of "high and certain dissolution curves in various media under strict dissolution test conditions", the correlation between in vitro dissolution test and in vivo bioavailability was improved, and the in vivo bioavailability test was gradually replaced or reduced. Promote drug manufacturers to conduct full and detailed research on preparation technology, so as to improve the success rate of bioavailability and clinical trials, or reduce bioavailability and clinical trials 4,5.
Dissolution test can effectively distinguish the difference of bioavailability of the same preparation. The key is how to establish the conditions of dissolution test.
Therefore, the Japanese National Drug evaluation department set up an expert group to determine the implementation plan and operation steps of the "Drug Quality Reevaluation" project, and compiled the dissolution test requirements and results of each variety (mainly for insoluble drugs) into a "Reference Catalog", which was published batch by batch for reference by Japanese drug manufacturers.
2.2 Operation Process of "Drug Quality Reevaluation" Project
2.2.1 Regulation of dissolution test conditions
In the above 4 dissolution media, paddle method is adopted, rotation speed is 50r/min,
The dissolution medium is 900ml, and the pH and rotational speed of the medium can be appropriately changed according to the actual situation or the addition of surfactants (organic solvents are not allowed to be added) for the test. The time points for the determination of common preparations were 5, 10, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120min, and then every 1h to 6 h. The time points for the determination of sustained-release preparations were 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 1 20 m i n, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24h, respectively. If the cumulative release rate of two consecutive points reached more than 95%, it could be terminated in advance.
2.2.2 Breed determination and pre-test
First of all, determine a batch of drug list (20 ~ 30 in each batch) and publish it on the special website of the "Reference Directory". Then the original manufacturer of the drug concerned will determine the dissolution curve of the factory product in the above four dissolution media and submit it to the expert panel. After communication with the original manufacturer, the team determined 4 "standard dissolution curves" and published them on the website. The imitation manufacturer shall determine the dissolution curves of the same varieties produced by the factory in the above four dissolution media according to this condition, and make a comparison before submitting it to the expert group. If so, it is approved; If not, an appropriate time limit shall be given to improve the preparation process; If not, the factory's approval to produce the drug is cancelled. Because the bioavailability of dissolution curves of different "slopes" is also different, the so-called "consistency" is not simply determined by visual measurement, but by similarity factor method (50 ≤ F2 ≤ 100) and Chow's method 6.
2.2.3 Result evaluation
(1) The expert Group will assign local drug testing institutions to conduct spot checks to verify the dissolution test data.
(2) If the generic manufacturer can produce a better dissolution curve or conditions, the expert Panel will consider whether to replace the standard preparation of the original manufacturer with the generic manufacturer's product as the reference preparation based on the bioavailability and clinical efficacy of the original manufacturer's product; If the drug of the original manufacturer has a good clinical effect, the products of both the original manufacturer and the imitation manufacturer shall be listed in the "Reference Catalog".
(3)) If necessary, in addition to the above four dissolution media, the dissolution measurement and comparison in the dissolution media with pH 2.0, 3.0 and 5.0 can be added.
(4) Dissolution test results should not be affected by instrument error, that is, should have good tolerance. If there are differences, it means that the preparation technology is not mature, still need to improve.
(5) In dissolution test, weak conditions (such as paddle method and speed 50r/min) should be selected as far as possible for formulation screening or comparison test between two preparations, while strong parameters (such as paddle method and speed 100r/min) should not be selected.
2.3 3 Publish the Reference Directory
In this directory, the following will be published: Active ingredient, type of preparation, specification of preparation, manufacturer of reference preparation, conditions of dissolution test, four standard dissolution curves, quality standard of dissolution test of the preparation, physical and chemical properties of the API (mainly including dissociation constant, solubility in four dissolution media, solution stability in water, different p and H solutions and light conditions, etc.).
2.4 Significance and impact
This project promoted the comprehensive and in-depth study and strict control of pharmaceutical process in Japanese pharmaceutical industry, improved the internal quality of drugs, and also played a role in promoting Japanese pharmaceutical enterprises to occupy the international market. Many enterprises are proud of the reference preparations, varieties can be included in the "Reference Catalog". At the same time, it has a great impact on small and medium-sized enterprises and plays a positive role in promoting the survival of the fittest in drug manufacturers. It also eliminates the idea that generic drugs are not as good as the original drugs and recognizes the quality of generic drugs. Japan adopts the principle that the price of drugs is set by the state and the price of the same preparation is the same throughout the country, but the government allows the price of the original drug or reference preparation manufacturer's product to be 10% ~ 20% higher than that of similar generic products. In addition, due to the large increase of dissolution test workload, the market demand for automatic dissolution instrument is very strong, but also indirectly promote the development and popularity of drug testing instruments. 2.5 Quality Assurance of Listed Products
In order to ensure that the quality of the late-stage mass-produced drug is the same as that of the clinical trial drug, the Japanese drug certification authority requires the manufacturer's internal control standards to test the sample in strict accordance with the requirements of the four dissolution curves (generally, the company only tests the most difficult dissolution curve). Local drug inspection offices carry out random tests. It can be seen that the Japanese drug evaluation department has formulated detailed, unified and scientific dissolution test conditions and dissolution limit requirements for each solid preparation of (insoluble) drugs, which avoids the "low-level duplication" of drug imitation and encourages pharmaceutical enterprises to conduct in-depth research on the preparation process, so that the supply of professionals related to drug preparation is in short supply. It also promotes the development of pharmaceutical auxiliary materials, pharmaceutical machinery and equipment and other industries. 3. Current situation of our country
At present, a variety that is not included in pharmacopoeia may have dozens of manufacturers, and there will be dozens of different quality standards. The dissolution test conditions are paddle plate method, the speed of 50 ~ 100r/ min, and the addition of surfactants and even organic solvents. In the process of research and development, the research unit often selects the product of a domestic pharmaceutical factory as the reference preparation. Even if some foreign preparations are selected as the reference preparation, the dissolution conditions are too loose, and usually only one dissolution medium is compared, and a variety of media are rarely compared. This has led to a tendency to assume that dissolution tests exist in isolation, with little regard for correlations with in vivo bioavailability. At present, many new drugs and generic drugs declared, as well as research articles on dissolution of solid preparations published in academic journals, have entered this "misunderstanding". It also resulted in the roughness and low-level repetition of the present preparation technology in our country. It also indirectly dampened the enthusiasm of enterprises to study the preparation technology further and formulate the strict dissolution test conditions. However, when the pharmacopoeia or standard of drug income is changed, the actual situation of each product is taken too much into account in the formulation of quality standards, so that most of the products produced by manufacturers can meet the specified dissolution test conditions. Many Chinese enterprises have passed GMP certification, and preparation process screening and dissolution test conditions is a professional knowledge, technology research, belongs to the category of "software". Therefore, enterprises and their products cannot be judged simply by whether they have passed GMP certification. At present, the number of generic drug applications is extremely large, and the drug evaluation center also has a heavy task. How to objectively evaluate whether its intrinsic quality is bioequivalent with imported preparations is worth our deep thought. In domestic bioavailability tests, young and healthy people are selected, and the results are easy to be consistent. But if you choose a different population, the situation may be different. 4 Suggestions and Prospects
It was pointed out in reference 7 that "reference catalogue of pharmaceutical preparations" should be established as soon as possible, and detailed reference rules should be provided. Products produced by one pharmaceutical factory or dissolution test conditions should not be randomly selected for comparison, because the final product may deviate far from the specified 80% error range. The State Food and Drug Administration has also implemented the "Action Plan to Improve National Drug Standards" since 2004. In the following three to five years, the State Food and Drug Administration will comprehensively clean up drugs with low standards and uncontrollable quality, and ensure the effectiveness of marketed drugs from the source. 4.1 Specific Suggestions
The "National Action Plan for Improving Drug Standards" can be closely linked with the establishment of our own reference preparation catalogue.
(1) An expert group shall be set up to form the committee of the Catalogue of Reference Preparations of Drugs. The committee shall determine a series of documents, such as working guidelines, guiding principles, technical details of dissolution determination, method certification principles, etc., and establish a special website to publish the corresponding plan and specific steps of implementation, so that the production enterprises can make certain preparations.
(2) The list of the first batch of drugs should be selected from insoluble drugs, pharmacopoeia varieties, varieties with high market demand and varieties with high patient population based on the accessibility of reference preparations. Publish the list of drug varieties to be evaluated batch by batch in an orderly manner.
(3) Reference preparations can be first established from the varieties produced by foreign famous pharmaceutical factories in domestic joint venture factories, and the factory shall first determine the four dissolution curves of the specified products. When certain requirements can be met, the varieties of the joint venture factory can be temporarily identified as reference preparations. Joint venture if does not produce reference preparation, can import preparation or the first domestic can meet the dissolution requirements of the manufacturer's products, as our reference preparation. If necessary, consideration may be given to the listed in the Japanese reference preparation list.
(4) Publish the list and catalog of the first batch of drugs and the corresponding "4 dissolution curve data" and the manufacturers of reference preparations on the website, and notify all manufacturers of these varieties in writing to reevaluate the dissolution test conditions and methods of our products within a certain period (such as 3 ~ 6 months), and improve the preparation process to meet the requirements of the dissolution curve in the catalog. Finally submit to the local drug inspection institute for review. If the manufacturer fails to meet the requirements within a certain period, it can postpone the deadline according to the actual situation. If it still fails to meet the requirements, it can cancel the production approval number of the product.
(5) Market spot check should be mainly based on the dissolution measurement, and the dissolution situation in the four dissolution media should be determined.
4.2 Outlook
Through the national drug evaluation department to strengthen the evaluation of dissolution test and gradually improve the standard, in line with the international, can promote our country The improvement of drug production technology, promoting drug production enterprises to in-depth study of preparation technology, promoting the development of higher pharmaceutical education, and pulling the development and progress of pharmaceutical excipients industry, pharmaceutical machinery equipment industry, and the integration of drug research and development companies, enterprise annexation market behavior, will also have a positive promoting role. In the current "centralized drug bidding and purchasing work", it is suggested to conduct scientific and effective in vitro dissolution test for similar varieties produced by multiple manufacturers. For drugs with good dissolution curve and dissolution degree, they should be the first choice to win the bid, so as to make the bidding easier to operate objectively and provide scientific guidance. In a word, dissolution test is the "soul" of solid drug preparation, seize this point, can "leverage" the overall development of the whole pharmaceutical industry and related industries.
Thanks to all the colleagues who have contributed valuable comments and suggestions to this article.
References:
1 Zhai Falin, Ding Qinglong, Yin Qiang. Study on dissolution of sulapride tablets J. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 1991, 11(5): 209-211. (in Chinese) 2Morihara M, Aoyagi N, Kaniwa N, et al. Assessment of gastric acidity of Japanese subjects over the last 15 yearsJ. Biol Pharm Bull , 2001, 24(3): 313-315. 3 Xue Daquan, Gao Hongci, Zhang Xianzhou. Guide for Preparation of Practical Tablets M. Hubei: Wuhan Press, 2000. 329-330. 4 Japan ministry medical 薬 security review management course. After 発 medical 薬 product の biology test of equality ン に つ い て M. Japanese medical 薬 review no. 487, 1997-12-22. 5 Japan ministry medical 薬 security review management course. Guidelines for the Study of bioequivalence of generic Drugs M. No.487, 1997-12-22. 6 Xia Jinhui, Liu Changxiao. Statistical evaluation and analysis of dissolution rate of solid drug preparation in vitro M. Chinese Journal of Pharmacy, 2000, 35(2): 130. (in Chinese) 7 Chen X Y. Discuss how to improve the quality of existing national standard drugs from the problems of bioequivalence study N. China Medical News, 2004-01-08.